School Discipline Disparities in Missouri's Public Schools
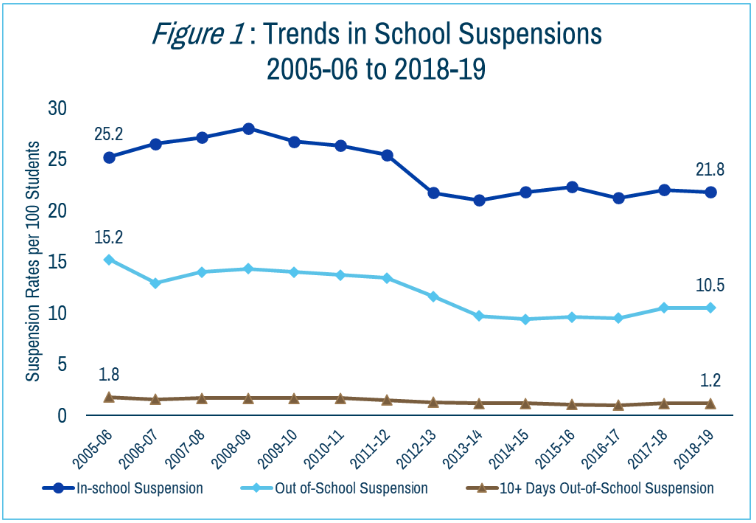
Using school-level data from Missouri’s Department of Elementary and Secondary Education from 2005 through 2019, we explored between-school disparities in out-of-school suspensions based on school characteristics - racial composition, locality, and socioeconomic status - to track trends and see if schools have made improvements. We find that over the last fourteen years, out-of-school suspension rates have declined, but large disparities persist between schools serving different populations of students. Out-of-school suspension rates are over five times higher for schools with predominantly (>75%) racial minorities than in schools with a majority of White students, four times higher for poorer communities than wealthier ones, and more than three times higher in urban schools than in rural ones.